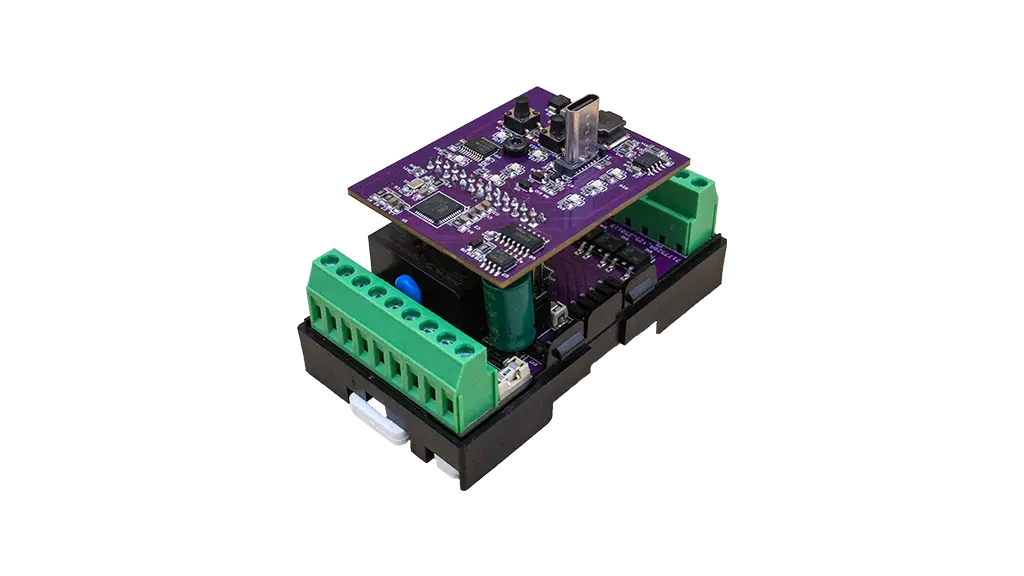
RGB-621-R1 RGBCCT Module
https://www.home-master.eu/shop/rgb-621-r1-rgbcct-module-57 https://www.home-master.eu/web/image/product.template/57/image_1920?unique=d6045d9The RGB-621-R1 offers fast and reliable lighting control via RS485 communication, delivering smooth dimming, scene management and intelligent automation. The robust electrical design ensures safe operation in control cabinets and distributed installations.
KEY BENEFITS:
- 5 PWM outputs for RGB + CW/WW LED strips
- RS485 Modbus RTU communication
- DIN-rail enclosure for easy installation
- High-power MOSFET outputs (up to 5A per channel)
- Onboard relay for LED power control
- Two isolated digital inputs
- USB-C configuration via WebConfig
- Works with Home Assistant and ESPHome
- Industrial-grade design with surge protection
- Can operate standalone or in PLC networks
Hardware Features & Control
This RGB LED controller provides five high-current PWM channels for controlling RGB lighting and tunable white LEDs. A built-in relay allows switching of power supplies or lighting zones, while two isolated digital inputs support wall switches, buttons or sensors.
Using RS485 Modbus RTU communication, the module receives commands from a PLC or automation controller. Configuration is done through USB-C using a browser-based WebConfig tool — no drivers or special software required.
Built for Reliability
The RGB-621-R1 uses an isolated dual-board architecture separating logic and power electronics for stable performance. Surge suppression, galvanic isolation, resettable fuses and transient protection ensure reliable operation in electrical cabinets and industrial environments.
Fail-safe logic retains the last lighting state if communication is lost, preventing unexpected lighting failures.
Home Assistant & ESPHome Integration
The RGB-621-R1 integrates smoothly into Home Assistant and ESPHome ecosystems. Lighting channels appear as controllable entities, enabling automation rules, scenes, dashboards and scripting.
Designed for Installers & Makers
Whether you’re deploying smart lighting in a commercial building or building DIY projects, this open-source RGB LED controller gives you total flexibility. No vendor lock-in. Full firmware access. Professional-grade hardware.
Back on Kickstarter
Be among the first to receive the HomeMaster products by backing our Kickstarter campaign.
- Early-bird rewards available while supplies last
- You’re only charged if the campaign reaches its goal
- Support reliable, local, open-source automation
Back on Kickstarter
Be among the first to receive the HomeMaster products by backing our Kickstarter campaign.
- Early-bird rewards available while supplies last
- You’re only charged if the campaign reaches its goal
- Support reliable, local, open-source automation
Display Name:
RGB-621-R1 RGBCCT Module
RGB-621-R1 — Module for RGB+CCT LED Control
HOMEMASTER – Modular control. Custom logic.
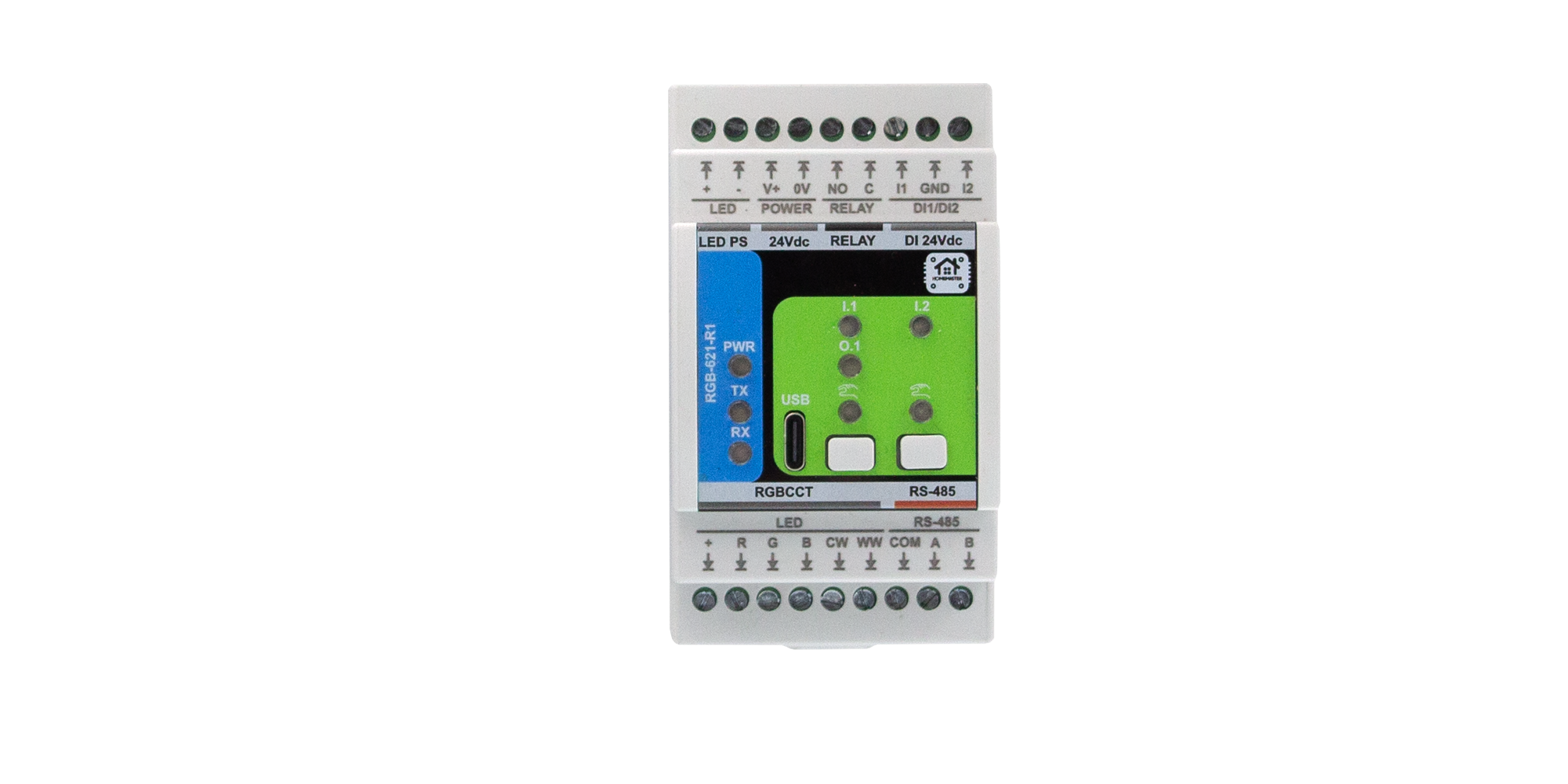

1. Introduction
1.1 Overview of the RGB-621-R1
The RGB-621-R1 is a smart RGB + CCT LED controller module designed for HomeMaster automation systems and other Modbus RTU networks.
It features 5 high-current PWM outputs for RGB and Tunable White (CCT) LED control, 2 isolated digital inputs for wall switches or sensors, and 1 relay output for switching external loads or LED drivers.
Powered by the Raspberry Pi RP2350A microcontroller, the module supports RS-485 (Modbus RTU) communication and configuration via WebConfig over USB-C (Web Serial) — no drivers or external software required.
It connects directly to HomeMaster MicroPLC and MiniPLC controllers or operates as a standalone Modbus slave in any automation network.
Its isolated I/O architecture, dual-board design, and built-in surge and short-circuit protection ensure accurate dimming, stable communication, and reliable operation in demanding home, ambient, or architectural lighting applications.
1.2 Features & Architecture
| Subsystem | Qty | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Inputs | 2 | Galvanically isolated (ISO1212) dry-contact inputs with surge and reverse protection |
| PWM Outputs | 5 | N-channel MOSFET drivers (AP9990GH-HF), 12 V / 24 V LED channels for R / G / B / CW / WW |
| Relay Output | 1 | SPST-NO relay (HF115F/005-1ZS3), 5 V coil, rated 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 VDC |
| Buttons | 2 | Local control or configuration triggers (SW1 / SW2) |
| LED Indicators | 8 | Power, TX/RX, input, and status LEDs for feedback and diagnostics |
| Modbus RTU | Yes | RS-485 interface via MAX485CSA+T transceiver; 120 Ω termination selectable |
| USB-C | Yes | WebConfig & firmware flashing with PRTR5V0U2X ESD protection |
| Power Input | 24 V DC | Protected by resettable fuses (1206L series), TVS (SMBJ33A), and reverse-blocking (STPS340U) |
| Logic Supply | — | AP64501SP-13 buck (5 V) + AMS1117-3.3 LDO chain |
| MCU | RP2350A | Dual-core Arm Cortex-M33 @ 133 MHz with 32 Mbit QSPI Flash (W25Q32JVUUIQ) |
| Isolation & Protection | — | Galvanic isolation, TVS diodes, PTC fuses, transient suppression on all field I/O |
Architecture summary:
- MCU Board: manages logic, USB, Modbus, and power regulation
- Field Board: contains LED drivers, relay circuit, and isolated input section
This modular, two-board design ensures clean signal separation between logic and 24 V field wiring, improving reliability in mixed-voltage installations.
1.3 System Role & Communication
The RGB-621-R1 operates as a Modbus RTU slave on an RS-485 differential bus, typically polled by a HomeMaster controller (MicroPLC / MiniPLC) or other Modbus master.
Each module is assigned a unique Modbus address via WebConfig, supporting up to 32 devices per bus.
Default communication parameters:
- Address: 1
- Baud rate: 19200 bps
- Format: 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit (8N1)
- Termination: 120 Ω enabled at end of bus
- Fail-safe: retains last valid PWM and relay state if communication is lost
The controller periodically polls holding registers to:
- Write PWM duty values for R, G, B, CW, WW channels
- Control the relay output
- Read digital input and status bits
WebConfig enables users to modify address, baud rate, test I/O, calibrate channels, and perform real-time diagnostics — simplifying setup and commissioning.
2. RGB-621-R1 — Technical Specification
2.1 Diagrams & Pinouts
| Diagram |
|---|
 <br>System Block Diagram <br>System Block Diagram |
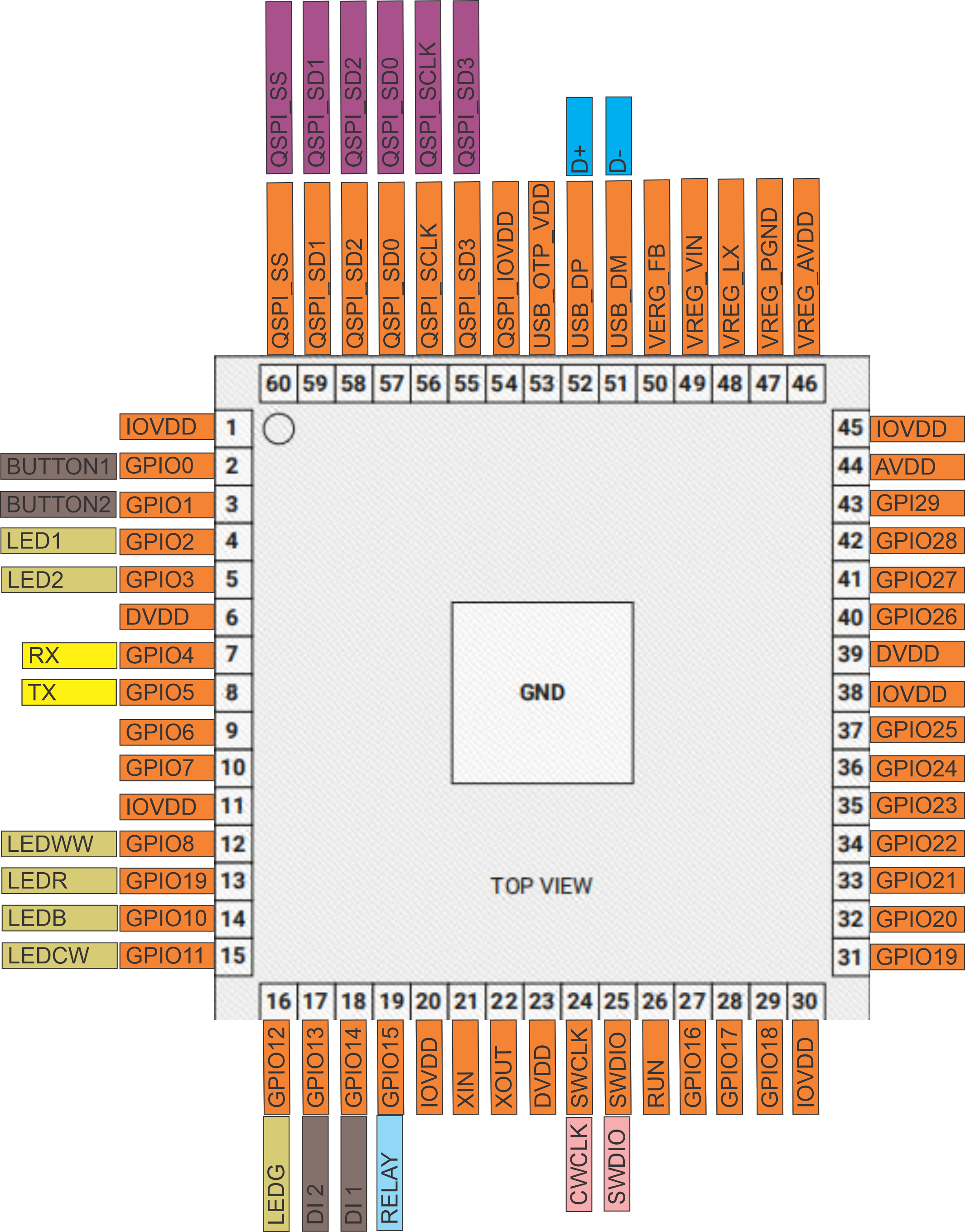 <br>RP2350A MCU Pinout <br>RP2350A MCU Pinout |
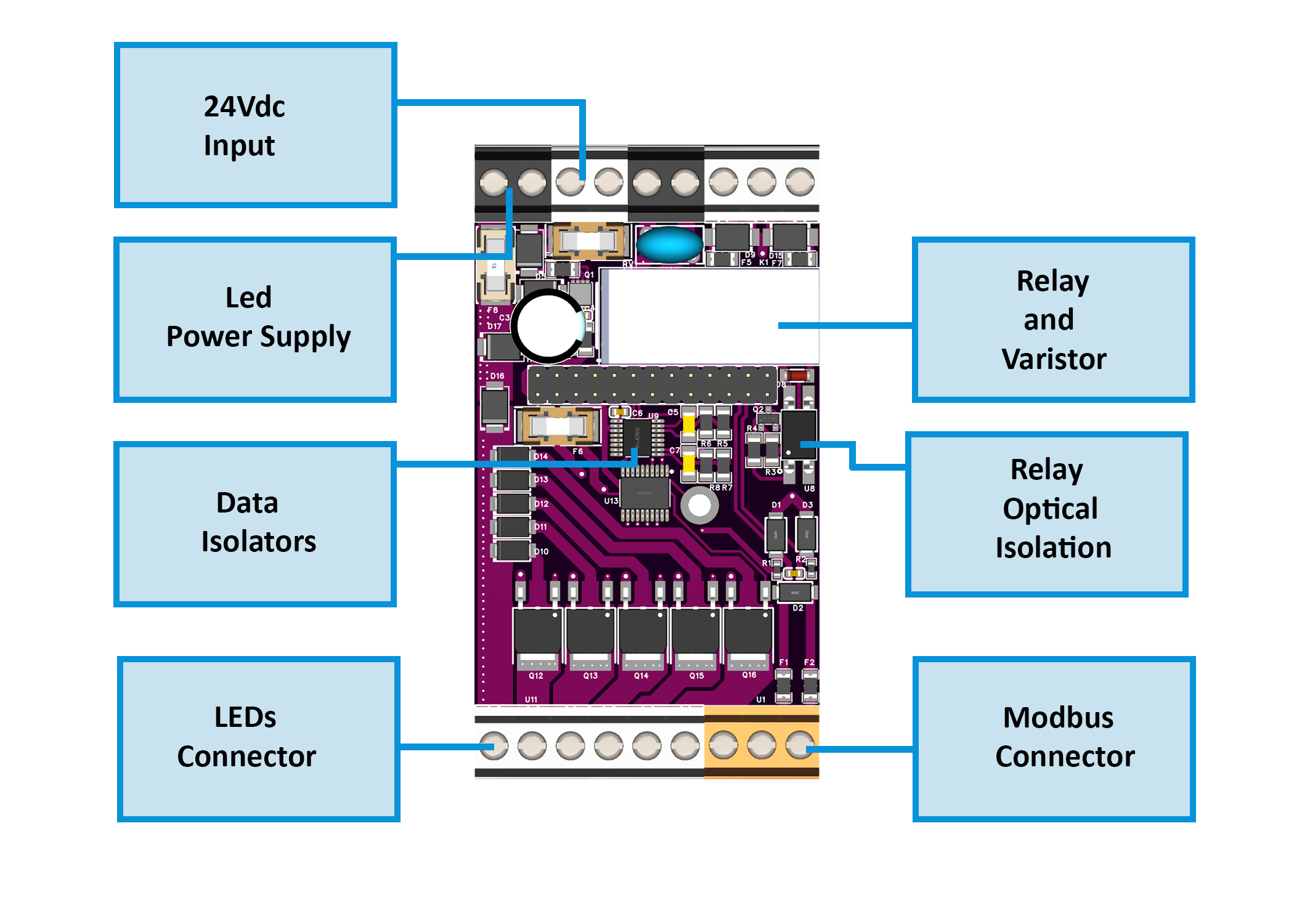 <br>Field Board Layout <br>Field Board Layout |
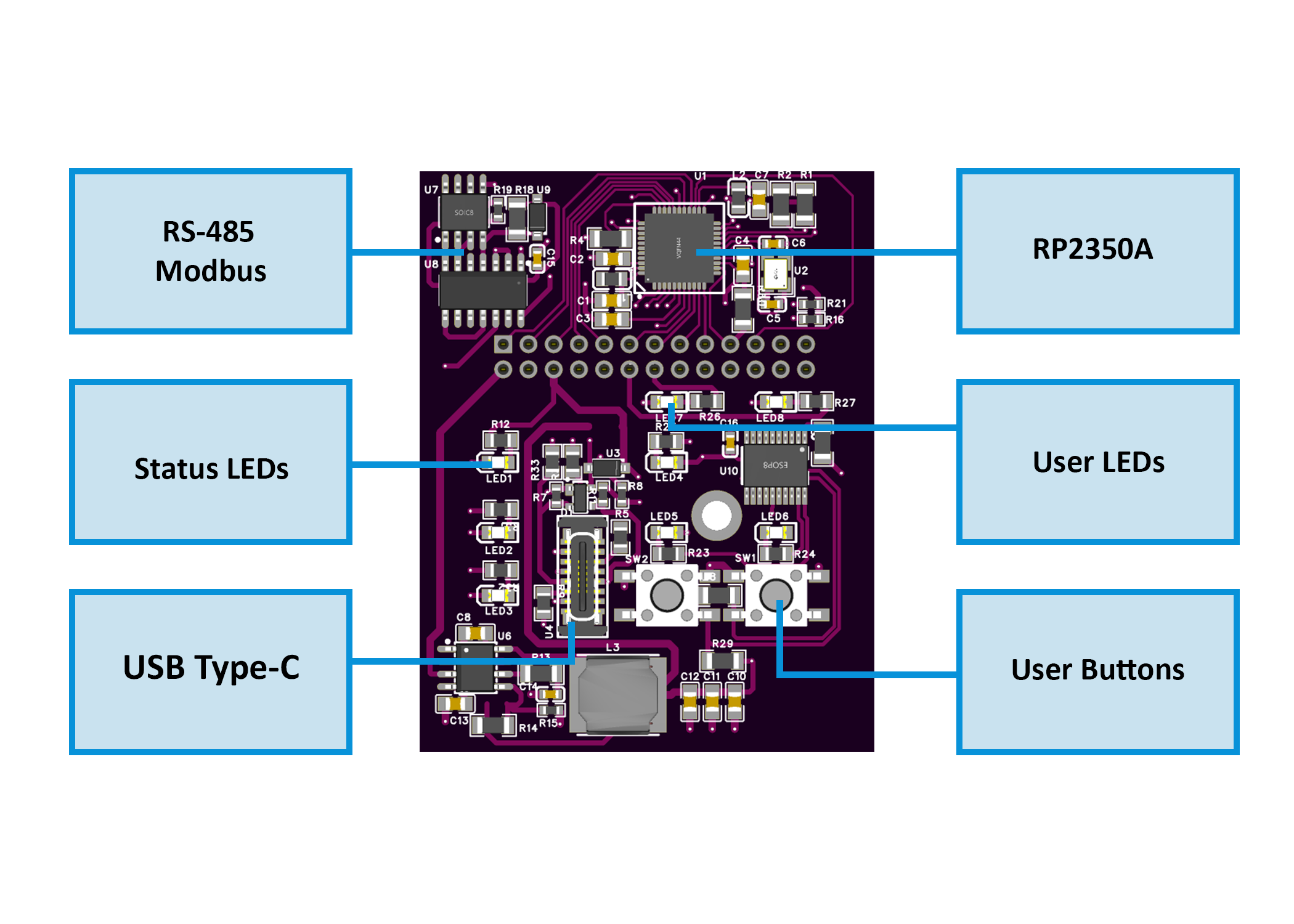 <br>MCU Board Layout <br>MCU Board Layout |
2.2 Overview
RGB + CCT LED controller with:
- 5 PWM outputs, 2 isolated digital inputs, 1 relay
- RS-485 (Modbus RTU) slave for HomeMaster controllers or SCADA
- Configurable via USB-C WebConfig
- Compact DIN-rail form factor
2.3 I/O Summary
| Interface | Qty | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Inputs | 2 | 24 V isolated (ISO1212), dry-contact or sourcing |
| Relay | 1 | SPST-NO, 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 VDC |
| PWM Outputs | 5 | Low-side MOSFETs (AP9990GH-HF) for R/G/B/CW/WW |
| RS-485 (Modbus) | 1 | MAX485 transceiver, 19200 bps 8N1 default |
| USB-C | 1 | Config & firmware upload (logic only) |
| MCU | 1 | RP2350A @ 133 MHz, 32 Mbit QSPI Flash |
| Buttons / LEDs | — | Local control, TX/RX & status indicators |
2.4 Terminals & Pinout

Top: V+/0 V (24 V DC input), Relay C/NO, Inputs I1/I2 (+ GND)
Bottom: PWM R/G/B/CW/WW (24 V COM +), RS-485 A/B (+ COM opt.)
2.5 Electrical & Environmental
- Supply: 24 V DC ±10 % (SELV/PELV), ≈ 2 W (no LED load)
- PWM Drive: up to 5 A per channel (25 A max total)
- Relay: 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC
- Isolation: 3 kVrms (inputs ↔ logic)
- RS-485: 19200 bps 8N1 (default), 115.2 kbps max
- USB-C: WebConfig / firmware only, ESD-protected
- Env.: 0 – 40 °C, ≤ 95 % RH non-condensing
2.6 MCU, Protections & Build
- MCU: Raspberry Pi RP2350A dual-core M33
- Storage: W25Q32 32 Mbit Flash
- Protections: PTC fuses, TVS diodes, reverse polarity & ESD networks
- Mounting: DIN-rail EN 50022 (35 mm), IP20 enclosure
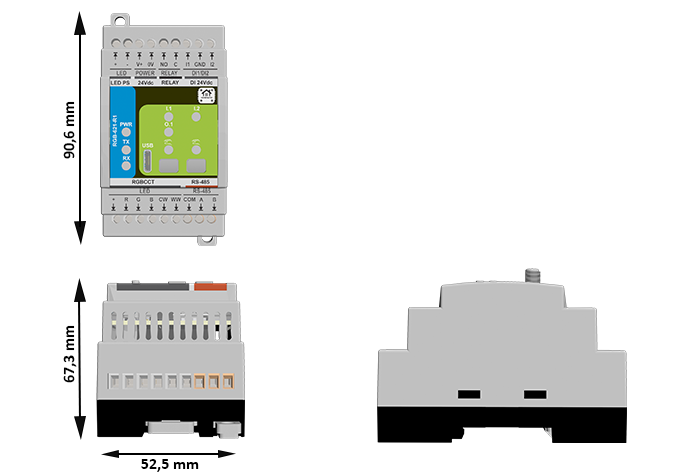
- Dimensions: 52.5 × 90.6 × 67.3 mm · Weight ≈ 0.25 kg
2.7 Absolute Ratings
| Parameter | Min | Typ | Max | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | 20 V | 24 V | 30 V | SELV input protected |
| Power Use | — | 1.85 W | 3.0 W | No LED load |
| Relay Contacts | — | — | 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC | Resistive |
| PWM Current | — | — | 5 A per ch | External PSU limited |
| RS-485 Rate | — | — | 115.2 kbps | Half-duplex |
| USB Voltage | 4.75 V | 5 V | 5.25 V | Logic only |
| Operating Temp | 0 °C | — | 40 °C | ≤ 95 % RH |
Installer Tip: Use upstream fusing and snubbers for inductive loads.
2.8 Firmware & Operation
- Operates as Modbus RTU slave
- Configurable via WebConfig (USB-C)
- Registers control PWM and Relay; inputs readable as coils/discretes
- Buttons: local test / override
- LED Indicators:
- PWR: Power OK
- TX/RX: Communication activity
- DI1/DI2: Input state
- RUN/ERR: Status / fault pattern
3. Use Cases
The RGB-621-R1 module is primarily designed for multi-channel lighting control but can also be used in broader automation and signaling tasks.
Its combination of isolated inputs, PWM outputs, and a relay makes it suitable for ambient lighting, architectural control, and user-interactive automation.
🏠 Use Case 1 — RGB Scene Control with Wall Switch Inputs
Purpose:
Use two wall switches to trigger and cycle through preset color or brightness scenes stored in the controller.
How it works:
Each digital input acts as a trigger to change the lighting mode or adjust brightness levels.
Setup Steps:
- Connect DI1 and DI2 to wall switches (dry contact).
- Wire RGBW LED strips to PWM outputs R, G, B, CW, WW.
- In WebConfig, assign Modbus address and test LED channels.
- In the MicroPLC / MiniPLC, define scene logic (e.g., DI1 → next scene, DI2 → off).
- Use Modbus holding registers to control PWM duty cycles for each channel.
💡 Use Case 2 — Relay-Based Power Switching for LED Drivers
Purpose:
Control a 24 V LED power supply or auxiliary lighting circuit via the onboard relay.
How it works:
The relay output switches the driver’s DC line or AC supply based on PLC logic or local input triggers.
Setup Steps:
- Connect the relay COM/NO terminals in series with the LED driver’s supply.
- Wire LED outputs to PWM channels for dimming control.
- In WebConfig, enable relay control via Modbus coil.
- Program the controller to energize the relay only when active scenes are running.
- Optionally, use a wall switch on DI1 as a manual override for relay control.
🌈 Use Case 3 — Tunable White (CCT) Control with Daylight Automation
Purpose:
Implement human-centric lighting that adjusts color temperature (CCT) throughout the day.
How it works:
Two PWM channels (CW and WW) mix warm and cool light based on time of day or ambient sensor input.
Setup Steps:
- Connect CW and WW LED strips to respective PWM outputs.
- Define a time-based profile in the controller (morning = warm, midday = cool).
- Use Modbus registers to update CW/WW duty cycles automatically.
- Optionally, map DI1 as a manual “Day/Night” mode toggle.
- Adjust max/min PWM limits in WebConfig for consistent brightness.
🚨 Use Case 4 — Status Indicator / Alarm Signaling
Purpose:
Display system or alarm status using color lighting patterns.
How it works:
The module’s PWM channels can drive RGB indicators or stack lights controlled by alarm flags from the PLC.
Setup Steps:
- Wire a small 12 V RGB LED indicator to PWM outputs R, G, and B.
- Connect the module to the same Modbus bus as the alarm controller.
- Assign registers to display alarm colors (e.g., red = alert, green = normal).
- Use DI1 as a manual alarm acknowledge input.
- Configure the relay as an auxiliary siren or warning signal driver.
🧠 Use Case 5 — Standalone Mood Lighting Controller
Purpose:
Operate ambient RGB lighting locally without an external PLC, using onboard inputs and preloaded logic.
How it works:
The module can store simple input-to-output mapping rules (through WebConfig or firmware) for local lighting control.
Setup Steps:
- Power the module from a 24 V DC supply.
- Connect LED strips to PWM outputs and wall switches to DI1/DI2.
- In WebConfig, set input-to-PWM mapping rules or fading behavior.
- Adjust brightness levels and transition speeds.
- Optionally, connect to Modbus later for centralized control or monitoring.
These examples illustrate how the RGB-621-R1 can serve as both a dedicated lighting driver and a multi-purpose automation node, combining smooth dimming, robust field isolation, and Modbus integration.
4. Safety Information
4.1 General Requirements
| Requirement | Detail |
|---|---|
| Qualified Personnel | Installation, wiring, and servicing must be performed by trained technicians familiar with 24 V DC SELV/PELV control systems. |
| Power Isolation | Always disconnect the 24 V DC supply and RS-485 network before wiring or servicing. |
| Rated Voltages Only | Operate only from a Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV/PELV) 24 V DC source. 12 V DC is not supported. Never connect mains (230 V AC) to any terminal. |
| Independent Power | Each controller and I/O module must have its own 24 V DC power supply, sized for its load and fused appropriately. |
| Grounding | Ensure proper protective-earth (PE) connection of the control cabinet and shielded bus cable. |
| Enclosure | Mount the device on a DIN rail inside a dry, clean enclosure. Avoid condensation, dust, or corrosive atmosphere. |
4.2 Installation Practices
DIN-Rail Mounting
- Mount on a 35 mm DIN rail (EN 60715).
- Provide at least 10 mm clearance above/below for airflow and terminal access.
- Route LED-power wiring separately from communication lines.
Electrical Domains
Two distinct domains exist:
- Field Power (24 V DC) — supplies LED drivers, relay, and input circuits.
- Logic Power (5 V / 3.3 V) — internal regulation for MCU, USB, and RS-485.
The field return is GND_FUSED; the logic return is GND.
🟡 Important: Do not externally bridge GND_FUSED and GND.
Isolation between these domains is provided internally through the ISO1212 and SFH6156 devices.
LED Power and Output Wiring
- The LED power rail (+24 V) enters through the protected input (fuses F3/F4, diode D5 STPS340U, surge D6 SMBJ33A).
- It passes the relay K1 (HF115F) and feeds the COM (+24 V) terminal on the bottom connector.
- LED channel outputs (R, G, B, CW, WW) are low-side PWM sinks using AP9990GH-HF MOSFETs.
- Connect LED + to COM, and each color cathode to its respective channel output.
- Only 24 V LED strips (common-anode type) are supported.
Relay Wiring
- Type HF115F (5 V coil, SPST-NO).
- Contact rating: 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC (resistive).
- For inductive loads, add an external flyback diode or RC snubber.
- Keep relay conductors away from signal wiring.
Digital Input Wiring
- Inputs use ISO1212 galvanic isolation.
- Connect dry contacts or 24 V DC sourcing sensors only.
- Each input path has a PTC fuse (F5/F6), TVS D9, and reverse diodes (D10–D14).
- Do not inject external voltage into DI pins.
- Use shielded twisted-pair cable for runs > 10 m.
4.3 Interface Warnings
⚡ Power Supply (24 V DC)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 24 V DC ± 10 % |
| Input Protection | PTC fuses (F1–F4), reverse-polarity diode (STPS340U), surge TVS (SMBJ33A) |
| Ground Reference | Field return GND_FUSED |
| Isolation | Field side isolated from logic via DC/DC and opto-devices |
| Notes | Use a regulated SELV 24 V DC supply rated ≥ 1 A per module. Each module must have its own isolated 24 V supply rail. |
🟢 Digital Inputs
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Type | Galvanically isolated, dry-contact or sourcing 24 V DC input |
| Circuit | ISO1212 receiver with TVS (SMBJ26CA) + PTC protection |
| Operating Range | 9 – 36 V DC (typ. 24 V DC) |
| Isolation | 3 kVrms (input ↔ logic) |
| Notes | For switches or sensors only; debounce handled in firmware. |
🔴 Relay Output
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Type | SPST-NO mechanical relay (HF115F/005-1ZS3) |
| Coil Voltage | 5 V DC (via SFH6156 optocoupler + S8050 driver) |
| Contact Rating | 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC (resistive) |
| Protection | External RC snubber / flyback diode recommended |
| Notes | Keep field wiring separate from logic; observe polarity and isolation boundaries. |
🔵 RS-485 Communication
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Transceiver | MAX485CSA+T |
| Bus Type | Differential, multi-drop (A/B lines) |
| Default Settings | 19200 bps · 8N1 |
| Termination | 120 Ω enabled only at end-of-line device |
| Protection | Surge/ESD network integrated |
| Notes | Observe polarity (A = +, B = –). Use shielded twisted-pair cable; ground shield at one end only. |
🧰 USB-C Interface
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Function | WebConfig setup & firmware update only |
| Protection | PRTR5V0U2X ESD + CG0603MLC-05E current limiters |
| Supply | 5 V DC from host computer (logic domain) |
| Isolation | Shares logic ground (GND); not isolated from RS-485 logic |
| Notes | Use only when field power is disconnected; not for continuous operation in field. |
⚠️ Important:
• The RGB-621-R1 operates only on 24 V DC SELV/PELV power.
• 12 V DC operation is not supported.
• Each module and controller has its own 24 V DC supply.
• Never connect mains voltage to any terminal.
• Maintain isolation betweenGND_FUSED(field) andGND(logic).
• Follow local electrical codes for fusing and grounding.
5. Installation & Quick Start
5.1 What You Need
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Module | RGB-621-R1 LED control module |
| Controller | HomeMaster MicroPLC / MiniPLC or any Modbus RTU master |
| Power Supply (PSU) | Regulated 24 V DC SELV/PELV, sized for module and LED load |
| Cables | 1× USB-C cable (for setup), 1× twisted-pair RS-485 cable |
| Software | Any Chromium-based browser (Chrome/Edge) with Web Serial support for WebConfig |
| Optional | Shielded wiring for long RS-485 runs, DIN-rail enclosure, terminal labels |
5.2 Power
-
The RGB-621-R1 operates exclusively from a 24 V DC SELV/PELV supply.
Connect the +24 V and 0 V (GND) to the top power terminals marked V+ and 0V or LED PS. -
The LED strip’s positive rail (+24 V) is routed internally through:
- PTC fuses (F3/F4) for over-current protection
- Reverse-polarity diode (STPS340U)
- Surge suppressor (SMBJ33A)
- Relay K1 (HF115F), which switches the LED power output (COM terminal)
The LED channels (R/G/B/CW/WW) act as low-side PWM sinks, and the LED strip must be 24 V common-anode.
-
Current consumption (typical):
- Logic + RS-485: ≈ 100 mA
- Relay coil: ≈ 30 mA (active)
- LED load: dependent on connected strips (sized per external 24 V LED PSU)
-
Ground references:
GND_FUSED→ field ground for LED and inputsGND→ logic/USB ground
These are internally isolated — do not tie them together externally.
4.3 Communication
RS-485 Pinout (bottom connector):
| Terminal | Signal | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | RS-485 A (+) | Non-inverting line |
| B | RS-485 B (–) | Inverting line |
| COM | Common reference (optional) | Field ground reference (GND_FUSED) for long bus runs |
-
Use a twisted-pair shielded cable (e.g., Cat-5 or RS-485 grade).
Connect the shield to protective earth (PE) at one end only. -
Network topology:
Daisy-chain (bus) — no star wiring.
Enable the 120 Ω termination resistor only at the last module in the chain. -
Default Modbus settings:
- Address: 1
- Baud rate: 19200 bps
- Data format: 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit (8N1)
-
Configuration:
- Connect via USB-C and open WebConfig in a Chromium-based browser.
- Set module address, baud rate, and optional relay/input parameters.
- Save settings to non-volatile memory.
-
Ground reference use:
- In most RS-485 systems, differential A/B are sufficient.
- The COM terminal may be connected between devices only if bus transceivers require a shared reference (rare in modern isolated networks).
⚙️ Quick Summary
- Mount the module on a DIN rail.
- Wire +24 V and 0 V to the LED PS terminals.
- Connect LED strips (common-anode to COM, cathodes to R/G/B/CW/WW).
- Wire RS-485 A/B to the controller.
- Plug in USB-C, open WebConfig, assign address, set baudrate, test outputs.
- Disconnect USB, power up the system, and verify Modbus communication.
5.4 Installation & Wiring
Use diagrams and explain:
- Inputs
- Relays
- Sensor rails (12/5V)
- RS-485 terminals
- USB port
5.5 Software & UI Configuration
Cover:
- WebConfig setup (address, baud)
- Input enable/invert/group
- Relay logic mode (group/manual)
- LED and Button mapping
5.6 Getting Started
Summarize steps in 3 phases:
- Wiring
- Configuration
- Integration
6. Modbus RTU Communication
Include:
- Address range and map
- Input/holding register layout
- Coil/discrete inputs
- Register use examples
- Polling recommendations
7. ESPHome Integration Guide
Only if supported. Cover:
- YAML setup (
uart,modbus,package) - Entity list (inputs, relays, buttons, LEDs)
- Acknowledge, override controls
- Home Assistant integration tips
8. Programming & Customization (RGB-621-R1)
8.1 Supported Languages
- Arduino (RP2350 core)
- C/C++ (PIO / SDK)
- MicroPython
8.2 Flashing
USB-C (Web Serial / CDC)
- Connect a USB-C cable from your PC to the module’s USB port.
- Enter BOOT mode: press Button 1 + Button 2 together (see photo below).
- Flash using PlatformIO or Arduino IDE (serial upload).
- When flashing completes, disconnect and power-cycle the module.
Reset: this module does not have a button combo for reset.
To reset, remove 24 VDC power for ≥5 s and re-apply.
PlatformIO / Arduino IDE setup
- Board/MCU: Raspberry Pi RP2350 / Generic RP235x
- USB upload: Serial (CDC)
- Flash layout (Arduino): e.g. 2 MB (Sketch 1 MB / FS 1 MB)
- Recommended libs (Arduino examples):
ModbusSerial(RTU master/slave helpers)Arduino_JSONLittleFSSimpleWebSerial(for WebConfig bridge)
Buttons reference (RGB-621-R1 front)
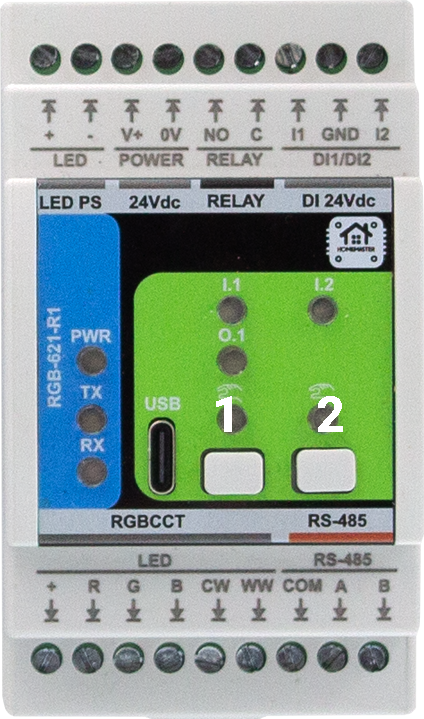

- Button 1 + Button 2 → BOOT mode
- Reset → power-cycle 24 VDC for ≥5 s
8.3 Firmware Updates
- Open the project in PlatformIO or Arduino IDE.
- Put device in BOOT (Button 1+2) and upload the new build.
- Configuration persistence: device settings (address/baud, channel trims, etc.) are stored in flash and kept across updates unless you explicitly erase.
- Recovery: if the device won’t enumerate, power-cycle 24 VDC (≥5 s) and retry BOOT (1+2). If needed, flash a minimal “factory” image first, then restore config via WebConfig backup.
9. Maintenance & Troubleshooting
9.1 Status LEDs (front panel)
| LED | Meaning |
|---|---|
| PWR | Steady when powered and firmware is running. |
| TX | Blinks on Modbus transmit. |
| RX | Blinks on Modbus receive. |
| I.1 / I.2 | Reflect isolated input states. |
| RUN/ERR (if present) | Heartbeat / fault pattern (refer to firmware notes). |
9.2 Resets & Modes
- BOOT mode: Button 1 + Button 2 (for flashing).
- Reset: remove 24 VDC for ≥5 s and re-apply.
9.3 Common Issues
- No communication (TX/RX dark):
Check A/B polarity, termination at bus ends (120 Ω), baud/ID match, and shared COM reference if separate PSUs. - Relay won’t trigger:
Confirm Modbus control vs. local override mode, verify coil/state in WebConfig, and ensure external wiring is on C/NO (dry contact). Add snubber for inductive loads. - LED channels do not light:
Verify COM (+24 V) to strip, channel cathodes on R/G/B/CW/WW, correct polarity, and adequate 24 V PSU sizing. - Inputs not detected:
Use DI 24Vdc terminals (I1/I2 with GND). Confirm sensor type (dry contact or 24 V sourcing) and debounce/invert settings in WebConfig. - USB not detected:
Use a data-capable USB-C cable; close any app holding the port; re-enter BOOT (1+2).
10. Open Source & Licensing
- Hardware: CERN-OHL-W v2
- Firmware: GPLv3
- Config Tools & examples: MIT (unless stated otherwise)
11. Downloads
- Repository (module path):
RGB-621-R1on GitHub - Firmware & examples:
RGB-621-R1/Firmware/ - WebConfig (HTML page):
RGB-621-R1/Firmware/ConfigToolPage.html - Schematics (PDF):
RGB-621-R1/Schematics/ - Datasheet & docs:
RGB-621-R1/Manuals/ - Images & diagrams:
RGB-621-R1/Images/
12. Support
- Official Support: https://www.home-master.eu/support
- WebConfig Tool (RGB-621-R1): https://www.home-master.eu/configtool-rgb-621-r1
- YouTube: https://youtube.com/@HomeMaster
- Hackster: https://hackster.io/homemaster
- Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/HomeMaster
- Instagram: https://instagram.com/home_master.eu
RGB-621-R1 — Module for RGB+CCT LED Control
HOMEMASTER – Modular control. Custom logic.

1. Introduction
1.1 Overview of the RGB-621-R1
The RGB-621-R1 is a smart RGB + CCT LED controller module designed for HomeMaster automation systems and other Modbus RTU networks.
It features 5 high-current PWM outputs for RGB and Tunable White (CCT) LED control, 2 isolated digital inputs for wall switches or sensors, and 1 relay output for switching external loads or LED drivers.
Powered by the Raspberry Pi RP2350A microcontroller, the module supports RS-485 (Modbus RTU) communication and configuration via WebConfig over USB-C (Web Serial) — no drivers or external software required.
It connects directly to HomeMaster MicroPLC and MiniPLC controllers or operates as a standalone Modbus slave in any automation network.
Its isolated I/O architecture, dual-board design, and built-in surge and short-circuit protection ensure accurate dimming, stable communication, and reliable operation in demanding home, ambient, or architectural lighting applications.
1.2 Features & Architecture
| Subsystem | Qty | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Inputs | 2 | Galvanically isolated (ISO1212) dry-contact inputs with surge and reverse protection |
| PWM Outputs | 5 | N-channel MOSFET drivers (AP9990GH-HF), 12 V / 24 V LED channels for R / G / B / CW / WW |
| Relay Output | 1 | SPST-NO relay (HF115F/005-1ZS3), 5 V coil, rated 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 VDC |
| Buttons | 2 | Local control or configuration triggers (SW1 / SW2) |
| LED Indicators | 8 | Power, TX/RX, input, and status LEDs for feedback and diagnostics |
| Modbus RTU | Yes | RS-485 interface via MAX485CSA+T transceiver; 120 Ω termination selectable |
| USB-C | Yes | WebConfig & firmware flashing with PRTR5V0U2X ESD protection |
| Power Input | 24 V DC | Protected by resettable fuses (1206L series), TVS (SMBJ33A), and reverse-blocking (STPS340U) |
| Logic Supply | — | AP64501SP-13 buck (5 V) + AMS1117-3.3 LDO chain |
| MCU | RP2350A | Dual-core Arm Cortex-M33 @ 133 MHz with 32 Mbit QSPI Flash (W25Q32JVUUIQ) |
| Isolation & Protection | — | Galvanic isolation, TVS diodes, PTC fuses, transient suppression on all field I/O |
Architecture summary:
- MCU Board: manages logic, USB, Modbus, and power regulation
- Field Board: contains LED drivers, relay circuit, and isolated input section
This modular, two-board design ensures clean signal separation between logic and 24 V field wiring, improving reliability in mixed-voltage installations.
1.3 System Role & Communication
The RGB-621-R1 operates as a Modbus RTU slave on an RS-485 differential bus, typically polled by a HomeMaster controller (MicroPLC / MiniPLC) or other Modbus master.
Each module is assigned a unique Modbus address via WebConfig, supporting up to 32 devices per bus.
Default communication parameters:
- Address: 1
- Baud rate: 19200 bps
- Format: 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit (8N1)
- Termination: 120 Ω enabled at end of bus
- Fail-safe: retains last valid PWM and relay state if communication is lost
The controller periodically polls holding registers to:
- Write PWM duty values for R, G, B, CW, WW channels
- Control the relay output
- Read digital input and status bits
WebConfig enables users to modify address, baud rate, test I/O, calibrate channels, and perform real-time diagnostics — simplifying setup and commissioning.
2. RGB-621-R1 — Technical Specification
2.1 Diagrams & Pinouts
| Diagram |
|---|
 <br>System Block Diagram <br>System Block Diagram |
 <br>RP2350A MCU Pinout <br>RP2350A MCU Pinout |
 <br>Field Board Layout <br>Field Board Layout |
 <br>MCU Board Layout <br>MCU Board Layout |
2.2 Overview
RGB + CCT LED controller with:
- 5 PWM outputs, 2 isolated digital inputs, 1 relay
- RS-485 (Modbus RTU) slave for HomeMaster controllers or SCADA
- Configurable via USB-C WebConfig
- Compact DIN-rail form factor
2.3 I/O Summary
| Interface | Qty | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Inputs | 2 | 24 V isolated (ISO1212), dry-contact or sourcing |
| Relay | 1 | SPST-NO, 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 VDC |
| PWM Outputs | 5 | Low-side MOSFETs (AP9990GH-HF) for R/G/B/CW/WW |
| RS-485 (Modbus) | 1 | MAX485 transceiver, 19200 bps 8N1 default |
| USB-C | 1 | Config & firmware upload (logic only) |
| MCU | 1 | RP2350A @ 133 MHz, 32 Mbit QSPI Flash |
| Buttons / LEDs | — | Local control, TX/RX & status indicators |
2.4 Terminals & Pinout

Top: V+/0 V (24 V DC input), Relay C/NO, Inputs I1/I2 (+ GND)
Bottom: PWM R/G/B/CW/WW (24 V COM +), RS-485 A/B (+ COM opt.)
2.5 Electrical & Environmental
- Supply: 24 V DC ±10 % (SELV/PELV), ≈ 2 W (no LED load)
- PWM Drive: up to 5 A per channel (25 A max total)
- Relay: 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC
- Isolation: 3 kVrms (inputs ↔ logic)
- RS-485: 19200 bps 8N1 (default), 115.2 kbps max
- USB-C: WebConfig / firmware only, ESD-protected
- Env.: 0 – 40 °C, ≤ 95 % RH non-condensing
2.6 MCU, Protections & Build
- MCU: Raspberry Pi RP2350A dual-core M33
- Storage: W25Q32 32 Mbit Flash
- Protections: PTC fuses, TVS diodes, reverse polarity & ESD networks
- Mounting: DIN-rail EN 50022 (35 mm), IP20 enclosure
- Dimensions: 52.5 × 90.6 × 67.3 mm · Weight ≈ 0.25 kg

2.7 Absolute Ratings
| Parameter | Min | Typ | Max | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | 20 V | 24 V | 30 V | SELV input protected |
| Power Use | — | 1.85 W | 3.0 W | No LED load |
| Relay Contacts | — | — | 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC | Resistive |
| PWM Current | — | — | 5 A per ch | External PSU limited |
| RS-485 Rate | — | — | 115.2 kbps | Half-duplex |
| USB Voltage | 4.75 V | 5 V | 5.25 V | Logic only |
| Operating Temp | 0 °C | — | 40 °C | ≤ 95 % RH |
Installer Tip: Use upstream fusing and snubbers for inductive loads.
2.8 Firmware & Operation
- Operates as Modbus RTU slave
- Configurable via WebConfig (USB-C)
- Registers control PWM and Relay; inputs readable as coils/discretes
- Buttons: local test / override
- LED Indicators:
- PWR: Power OK
- TX/RX: Communication activity
- DI1/DI2: Input state
- RUN/ERR: Status / fault pattern
3. Use Cases
The RGB-621-R1 module is primarily designed for multi-channel lighting control but can also be used in broader automation and signaling tasks.
Its combination of isolated inputs, PWM outputs, and a relay makes it suitable for ambient lighting, architectural control, and user-interactive automation.
🏠 Use Case 1 — RGB Scene Control with Wall Switch Inputs
Purpose:
Use two wall switches to trigger and cycle through preset color or brightness scenes stored in the controller.
How it works:
Each digital input acts as a trigger to change the lighting mode or adjust brightness levels.
Setup Steps:
- Connect DI1 and DI2 to wall switches (dry contact).
- Wire RGBW LED strips to PWM outputs R, G, B, CW, WW.
- In WebConfig, assign Modbus address and test LED channels.
- In the MicroPLC / MiniPLC, define scene logic (e.g., DI1 → next scene, DI2 → off).
- Use Modbus holding registers to control PWM duty cycles for each channel.
💡 Use Case 2 — Relay-Based Power Switching for LED Drivers
Purpose:
Control a 24 V LED power supply or auxiliary lighting circuit via the onboard relay.
How it works:
The relay output switches the driver’s DC line or AC supply based on PLC logic or local input triggers.
Setup Steps:
- Connect the relay COM/NO terminals in series with the LED driver’s supply.
- Wire LED outputs to PWM channels for dimming control.
- In WebConfig, enable relay control via Modbus coil.
- Program the controller to energize the relay only when active scenes are running.
- Optionally, use a wall switch on DI1 as a manual override for relay control.
🌈 Use Case 3 — Tunable White (CCT) Control with Daylight Automation
Purpose:
Implement human-centric lighting that adjusts color temperature (CCT) throughout the day.
How it works:
Two PWM channels (CW and WW) mix warm and cool light based on time of day or ambient sensor input.
Setup Steps:
- Connect CW and WW LED strips to respective PWM outputs.
- Define a time-based profile in the controller (morning = warm, midday = cool).
- Use Modbus registers to update CW/WW duty cycles automatically.
- Optionally, map DI1 as a manual “Day/Night” mode toggle.
- Adjust max/min PWM limits in WebConfig for consistent brightness.
🚨 Use Case 4 — Status Indicator / Alarm Signaling
Purpose:
Display system or alarm status using color lighting patterns.
How it works:
The module’s PWM channels can drive RGB indicators or stack lights controlled by alarm flags from the PLC.
Setup Steps:
- Wire a small 12 V RGB LED indicator to PWM outputs R, G, and B.
- Connect the module to the same Modbus bus as the alarm controller.
- Assign registers to display alarm colors (e.g., red = alert, green = normal).
- Use DI1 as a manual alarm acknowledge input.
- Configure the relay as an auxiliary siren or warning signal driver.
🧠 Use Case 5 — Standalone Mood Lighting Controller
Purpose:
Operate ambient RGB lighting locally without an external PLC, using onboard inputs and preloaded logic.
How it works:
The module can store simple input-to-output mapping rules (through WebConfig or firmware) for local lighting control.
Setup Steps:
- Power the module from a 24 V DC supply.
- Connect LED strips to PWM outputs and wall switches to DI1/DI2.
- In WebConfig, set input-to-PWM mapping rules or fading behavior.
- Adjust brightness levels and transition speeds.
- Optionally, connect to Modbus later for centralized control or monitoring.
These examples illustrate how the RGB-621-R1 can serve as both a dedicated lighting driver and a multi-purpose automation node, combining smooth dimming, robust field isolation, and Modbus integration.
4. Safety Information
4.1 General Requirements
| Requirement | Detail |
|---|---|
| Qualified Personnel | Installation, wiring, and servicing must be performed by trained technicians familiar with 24 V DC SELV/PELV control systems. |
| Power Isolation | Always disconnect the 24 V DC supply and RS-485 network before wiring or servicing. |
| Rated Voltages Only | Operate only from a Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV/PELV) 24 V DC source. 12 V DC is not supported. Never connect mains (230 V AC) to any terminal. |
| Independent Power | Each controller and I/O module must have its own 24 V DC power supply, sized for its load and fused appropriately. |
| Grounding | Ensure proper protective-earth (PE) connection of the control cabinet and shielded bus cable. |
| Enclosure | Mount the device on a DIN rail inside a dry, clean enclosure. Avoid condensation, dust, or corrosive atmosphere. |
4.2 Installation Practices
DIN-Rail Mounting
- Mount on a 35 mm DIN rail (EN 60715).
- Provide at least 10 mm clearance above/below for airflow and terminal access.
- Route LED-power wiring separately from communication lines.
Electrical Domains
Two distinct domains exist:
- Field Power (24 V DC) — supplies LED drivers, relay, and input circuits.
- Logic Power (5 V / 3.3 V) — internal regulation for MCU, USB, and RS-485.
The field return is GND_FUSED; the logic return is GND.
🟡 Important: Do not externally bridge GND_FUSED and GND.
Isolation between these domains is provided internally through the ISO1212 and SFH6156 devices.
LED Power and Output Wiring
- The LED power rail (+24 V) enters through the protected input (fuses F3/F4, diode D5 STPS340U, surge D6 SMBJ33A).
- It passes the relay K1 (HF115F) and feeds the COM (+24 V) terminal on the bottom connector.
- LED channel outputs (R, G, B, CW, WW) are low-side PWM sinks using AP9990GH-HF MOSFETs.
- Connect LED + to COM, and each color cathode to its respective channel output.
- Only 24 V LED strips (common-anode type) are supported.
Relay Wiring
- Type HF115F (5 V coil, SPST-NO).
- Contact rating: 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC (resistive).
- For inductive loads, add an external flyback diode or RC snubber.
- Keep relay conductors away from signal wiring.
Digital Input Wiring
- Inputs use ISO1212 galvanic isolation.
- Connect dry contacts or 24 V DC sourcing sensors only.
- Each input path has a PTC fuse (F5/F6), TVS D9, and reverse diodes (D10–D14).
- Do not inject external voltage into DI pins.
- Use shielded twisted-pair cable for runs > 10 m.
4.3 Interface Warnings
⚡ Power Supply (24 V DC)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 24 V DC ± 10 % |
| Input Protection | PTC fuses (F1–F4), reverse-polarity diode (STPS340U), surge TVS (SMBJ33A) |
| Ground Reference | Field return GND_FUSED |
| Isolation | Field side isolated from logic via DC/DC and opto-devices |
| Notes | Use a regulated SELV 24 V DC supply rated ≥ 1 A per module. Each module must have its own isolated 24 V supply rail. |
🟢 Digital Inputs
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Type | Galvanically isolated, dry-contact or sourcing 24 V DC input |
| Circuit | ISO1212 receiver with TVS (SMBJ26CA) + PTC protection |
| Operating Range | 9 – 36 V DC (typ. 24 V DC) |
| Isolation | 3 kVrms (input ↔ logic) |
| Notes | For switches or sensors only; debounce handled in firmware. |
🔴 Relay Output
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Type | SPST-NO mechanical relay (HF115F/005-1ZS3) |
| Coil Voltage | 5 V DC (via SFH6156 optocoupler + S8050 driver) |
| Contact Rating | 16 A @ 250 VAC / 30 V DC (resistive) |
| Protection | External RC snubber / flyback diode recommended |
| Notes | Keep field wiring separate from logic; observe polarity and isolation boundaries. |
🔵 RS-485 Communication
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Transceiver | MAX485CSA+T |
| Bus Type | Differential, multi-drop (A/B lines) |
| Default Settings | 19200 bps · 8N1 |
| Termination | 120 Ω enabled only at end-of-line device |
| Protection | Surge/ESD network integrated |
| Notes | Observe polarity (A = +, B = –). Use shielded twisted-pair cable; ground shield at one end only. |
🧰 USB-C Interface
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Function | WebConfig setup & firmware update only |
| Protection | PRTR5V0U2X ESD + CG0603MLC-05E current limiters |
| Supply | 5 V DC from host computer (logic domain) |
| Isolation | Shares logic ground (GND); not isolated from RS-485 logic |
| Notes | Use only when field power is disconnected; not for continuous operation in field. |
⚠️ Important:
• The RGB-621-R1 operates only on 24 V DC SELV/PELV power.
• 12 V DC operation is not supported.
• Each module and controller has its own 24 V DC supply.
• Never connect mains voltage to any terminal.
• Maintain isolation betweenGND_FUSED(field) andGND(logic).
• Follow local electrical codes for fusing and grounding.
5. Installation & Quick Start
5.1 What You Need
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Module | RGB-621-R1 LED control module |
| Controller | HomeMaster MicroPLC / MiniPLC or any Modbus RTU master |
| Power Supply (PSU) | Regulated 24 V DC SELV/PELV, sized for module and LED load |
| Cables | 1× USB-C cable (for setup), 1× twisted-pair RS-485 cable |
| Software | Any Chromium-based browser (Chrome/Edge) with Web Serial support for WebConfig |
| Optional | Shielded wiring for long RS-485 runs, DIN-rail enclosure, terminal labels |
5.2 Power
-
The RGB-621-R1 operates exclusively from a 24 V DC SELV/PELV supply.
Connect the +24 V and 0 V (GND) to the top power terminals marked V+ and 0V or LED PS. -
The LED strip’s positive rail (+24 V) is routed internally through:
- PTC fuses (F3/F4) for over-current protection
- Reverse-polarity diode (STPS340U)
- Surge suppressor (SMBJ33A)
- Relay K1 (HF115F), which switches the LED power output (COM terminal)
The LED channels (R/G/B/CW/WW) act as low-side PWM sinks, and the LED strip must be 24 V common-anode.
-
Current consumption (typical):
- Logic + RS-485: ≈ 100 mA
- Relay coil: ≈ 30 mA (active)
- LED load: dependent on connected strips (sized per external 24 V LED PSU)
-
Ground references:
GND_FUSED→ field ground for LED and inputsGND→ logic/USB ground
These are internally isolated — do not tie them together externally.
4.3 Communication
RS-485 Pinout (bottom connector):
| Terminal | Signal | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | RS-485 A (+) | Non-inverting line |
| B | RS-485 B (–) | Inverting line |
| COM | Common reference (optional) | Field ground reference (GND_FUSED) for long bus runs |
-
Use a twisted-pair shielded cable (e.g., Cat-5 or RS-485 grade).
Connect the shield to protective earth (PE) at one end only. -
Network topology:
Daisy-chain (bus) — no star wiring.
Enable the 120 Ω termination resistor only at the last module in the chain. -
Default Modbus settings:
- Address: 1
- Baud rate: 19200 bps
- Data format: 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit (8N1)
-
Configuration:
- Connect via USB-C and open WebConfig in a Chromium-based browser.
- Set module address, baud rate, and optional relay/input parameters.
- Save settings to non-volatile memory.
-
Ground reference use:
- In most RS-485 systems, differential A/B are sufficient.
- The COM terminal may be connected between devices only if bus transceivers require a shared reference (rare in modern isolated networks).
⚙️ Quick Summary
- Mount the module on a DIN rail.
- Wire +24 V and 0 V to the LED PS terminals.
- Connect LED strips (common-anode to COM, cathodes to R/G/B/CW/WW).
- Wire RS-485 A/B to the controller.
- Plug in USB-C, open WebConfig, assign address, set baudrate, test outputs.
- Disconnect USB, power up the system, and verify Modbus communication.
5.4 Installation & Wiring
Use diagrams and explain:
- Inputs
- Relays
- Sensor rails (12/5V)
- RS-485 terminals
- USB port
5.5 Software & UI Configuration
Cover:
- WebConfig setup (address, baud)
- Input enable/invert/group
- Relay logic mode (group/manual)
- LED and Button mapping
5.6 Getting Started
Summarize steps in 3 phases:
- Wiring
- Configuration
- Integration
6. Modbus RTU Communication
Include:
- Address range and map
- Input/holding register layout
- Coil/discrete inputs
- Register use examples
- Polling recommendations
7. ESPHome Integration Guide
Only if supported. Cover:
- YAML setup (
uart,modbus,package) - Entity list (inputs, relays, buttons, LEDs)
- Acknowledge, override controls
- Home Assistant integration tips
8. Programming & Customization (RGB-621-R1)
8.1 Supported Languages
- Arduino (RP2350 core)
- C/C++ (PIO / SDK)
- MicroPython
8.2 Flashing
USB-C (Web Serial / CDC)
- Connect a USB-C cable from your PC to the module’s USB port.
- Enter BOOT mode: press Button 1 + Button 2 together (see photo below).
- Flash using PlatformIO or Arduino IDE (serial upload).
- When flashing completes, disconnect and power-cycle the module.
Reset: this module does not have a button combo for reset.
To reset, remove 24 VDC power for ≥5 s and re-apply.
PlatformIO / Arduino IDE setup
- Board/MCU: Raspberry Pi RP2350 / Generic RP235x
- USB upload: Serial (CDC)
- Flash layout (Arduino): e.g. 2 MB (Sketch 1 MB / FS 1 MB)
- Recommended libs (Arduino examples):
ModbusSerial(RTU master/slave helpers)Arduino_JSONLittleFSSimpleWebSerial(for WebConfig bridge)
Buttons reference (RGB-621-R1 front)

- Button 1 + Button 2 → BOOT mode
- Reset → power-cycle 24 VDC for ≥5 s
8.3 Firmware Updates
- Open the project in PlatformIO or Arduino IDE.
- Put device in BOOT (Button 1+2) and upload the new build.
- Configuration persistence: device settings (address/baud, channel trims, etc.) are stored in flash and kept across updates unless you explicitly erase.
- Recovery: if the device won’t enumerate, power-cycle 24 VDC (≥5 s) and retry BOOT (1+2). If needed, flash a minimal “factory” image first, then restore config via WebConfig backup.
9. Maintenance & Troubleshooting
9.1 Status LEDs (front panel)
| LED | Meaning |
|---|---|
| PWR | Steady when powered and firmware is running. |
| TX | Blinks on Modbus transmit. |
| RX | Blinks on Modbus receive. |
| I.1 / I.2 | Reflect isolated input states. |
| RUN/ERR (if present) | Heartbeat / fault pattern (refer to firmware notes). |
9.2 Resets & Modes
- BOOT mode: Button 1 + Button 2 (for flashing).
- Reset: remove 24 VDC for ≥5 s and re-apply.
9.3 Common Issues
- No communication (TX/RX dark):
Check A/B polarity, termination at bus ends (120 Ω), baud/ID match, and shared COM reference if separate PSUs. - Relay won’t trigger:
Confirm Modbus control vs. local override mode, verify coil/state in WebConfig, and ensure external wiring is on C/NO (dry contact). Add snubber for inductive loads. - LED channels do not light:
Verify COM (+24 V) to strip, channel cathodes on R/G/B/CW/WW, correct polarity, and adequate 24 V PSU sizing. - Inputs not detected:
Use DI 24Vdc terminals (I1/I2 with GND). Confirm sensor type (dry contact or 24 V sourcing) and debounce/invert settings in WebConfig. - USB not detected:
Use a data-capable USB-C cable; close any app holding the port; re-enter BOOT (1+2).
10. Open Source & Licensing
- Hardware: CERN-OHL-W v2
- Firmware: GPLv3
- Config Tools & examples: MIT (unless stated otherwise)
11. Downloads
- Repository (module path):
RGB-621-R1on GitHub - Firmware & examples:
RGB-621-R1/Firmware/ - WebConfig (HTML page):
RGB-621-R1/Firmware/ConfigToolPage.html - Schematics (PDF):
RGB-621-R1/Schematics/ - Datasheet & docs:
RGB-621-R1/Manuals/ - Images & diagrams:
RGB-621-R1/Images/
12. Support
- Official Support: https://www.home-master.eu/support
- WebConfig Tool (RGB-621-R1): https://www.home-master.eu/configtool-rgb-621-r1
- YouTube: https://youtube.com/@HomeMaster
- Hackster: https://hackster.io/homemaster
- Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/HomeMaster
- Instagram: https://instagram.com/home_master.eu